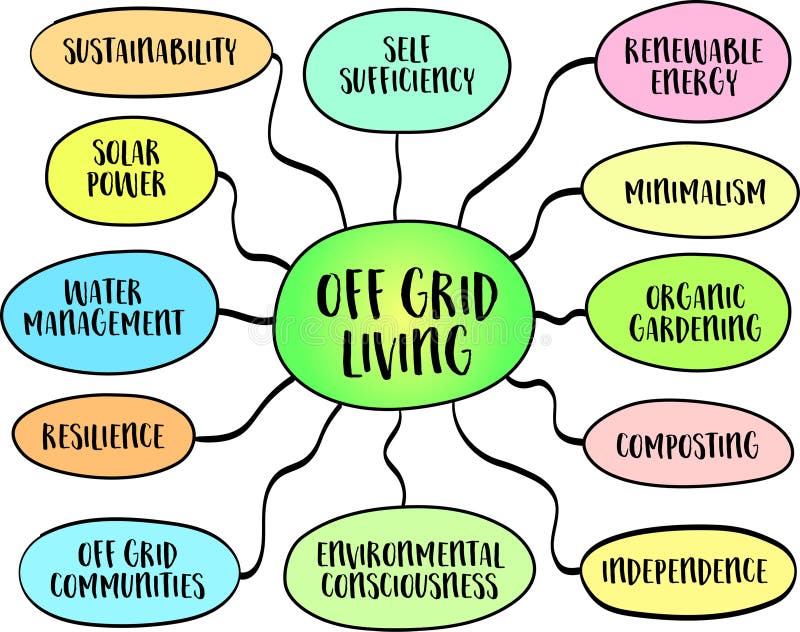
Green living off grid represents a compelling movement towards self-sufficiency and environmental responsibility. This lifestyle, increasingly popular among those seeking a simpler, more sustainable existence, involves minimizing reliance on traditional utilities and embracing renewable energy sources. From harnessing solar power to implementing efficient water management systems, individuals and communities are pioneering innovative approaches to living in harmony with nature, creating a model for a more environmentally conscious future.
This exploration delves into the practical aspects, challenges, and rewards of this transformative way of life.
The core principles involve designing and maintaining a home and lifestyle that minimizes environmental impact while simultaneously reducing reliance on external infrastructure. This includes generating your own power through renewable sources, harvesting and purifying your own water, and implementing effective waste management strategies, including composting. The article will examine various successful models, showcasing practical solutions for energy production, water conservation, and waste reduction, all while exploring the economic and social considerations involved in embracing this increasingly popular lifestyle choice.
Defining “Green Living Off Grid”
Green living off-grid represents a sustainable lifestyle characterized by minimizing environmental impact while relying on self-sufficiency for essential resources. This involves a conscious effort to reduce reliance on external infrastructure and utilities, opting instead for renewable energy sources, water conservation techniques, and responsible waste management.
Core Principles of Green Living
Green living centers around minimizing environmental footprint through conscious consumption, renewable resource utilization, and waste reduction. Key principles include reducing energy consumption, conserving water, minimizing waste generation, and promoting biodiversity.
Essential Components of Off-Grid Living
Off-grid living necessitates self-sufficiency in energy, water, and waste management. This typically involves the installation of renewable energy systems, implementation of water harvesting and purification methods, and establishment of composting or other waste disposal systems. Food production is often integrated, through gardening or other means.
Comparing Approaches to Combining Green Living and Off-Grid Existence
Several approaches exist, ranging from fully self-sufficient homesteads to partially off-grid lifestyles incorporating some grid-connected utilities. Fully off-grid systems prioritize complete independence, while partially off-grid systems might use the grid for backup power or certain services. The chosen approach depends on factors like location, budget, and personal preferences.
Examples of Successful Green Off-Grid Communities or Individuals
Numerous examples showcase successful green off-grid living. Many individuals and communities have demonstrated the feasibility and benefits of this lifestyle, adapting their approaches to suit diverse geographical and climatic conditions. Information on specific examples can be found through online searches and relevant literature.
| Location | Energy Source | Water Source | Waste Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rural Vermont, USA | Solar, Wind | Well, Rainwater Harvesting | Composting, Recycling |
| Off-grid community in New Mexico, USA | Solar, Wind | Well, Rainwater Harvesting | Composting, greywater recycling |
| Island community in the Pacific Ocean | Solar, Hydro | Rainwater Harvesting | Composting, Ocean Disposal (with careful consideration) |
| Rural area in Australia | Solar | Bore Water | Composting, Recycling |
Energy Solutions for Green Off-Grid Living
Source: dreamstime.com
Renewable energy sources are crucial for off-grid living. Careful consideration of energy needs, available resources, and system maintenance is essential for a successful implementation.
Embracing green living off-grid requires careful planning and resource management, focusing on sustainable energy sources and minimal environmental impact. For those curious about the lifestyle’s challenges and rewards, a look at cinematic portrayals can be insightful; check out this list of off grid living movies for a glimpse into various experiences. Ultimately, successful green off-grid living hinges on self-sufficiency and a deep respect for the natural world.
Renewable Energy Sources for Off-Grid Use
Solar, wind, and hydro power are the most common renewable energy sources for off-grid systems. Each offers unique advantages and disadvantages depending on location and environmental conditions.
- Solar Power:
- Advantages: Abundant sunlight in many areas, relatively low maintenance.
- Disadvantages: Intermittent energy source (dependent on weather), requires significant initial investment.
- Wind Power:
- Advantages: Consistent energy source in windy areas, relatively low maintenance.
- Disadvantages: Requires significant wind speeds, can be noisy, potential visual impact.
- Hydro Power:
- Advantages: Consistent energy source, minimal environmental impact (compared to fossil fuels).
- Disadvantages: Requires a reliable water source, potential environmental impact on aquatic ecosystems, significant initial investment.
Sample Off-Grid Energy System for a Small Dwelling
A small dwelling might utilize a combination of solar panels (e.g., 3kW system), a wind turbine (if location permits), and a battery bank (e.g., 10kWh capacity). System sizing depends on energy consumption, available resources, and budget. Professional consultation is advisable.
Energy Storage Solutions and Lifespan Considerations
Battery banks are essential for storing excess energy generated during peak hours for use during periods of low generation. Battery lifespan varies depending on technology and usage. Regular maintenance and replacement are necessary.
Environmental Impact of Different Renewable Energy Options
The environmental impact of renewable energy sources is significantly lower than fossil fuels. However, each option has some environmental footprint, including manufacturing, transportation, and end-of-life disposal considerations.
Water Management in Green Off-Grid Systems
Reliable water sources and efficient management are crucial for off-grid living. Water conservation is paramount given the limited availability of water in many off-grid locations.
Reliable Water Sources for Off-Grid Living
Rainwater harvesting and wells are common water sources. The suitability of each depends on factors such as rainfall patterns, geological conditions, and water quality.
Water Purification and Filtration Methods
Various methods exist for purifying and filtering water, including boiling, filtration systems (e.g., ceramic filters, sand filters), and UV sterilization. The choice depends on the source water quality and budget.
Best Practices for Water Conservation
Water conservation is crucial in off-grid settings. Strategies include low-flow showerheads, efficient irrigation systems, and greywater recycling (reusing wastewater for non-potable purposes).
Simple Rainwater Harvesting System Design
A simple system involves a roof catchment area, gutters, downspouts, a storage tank (e.g., a large plastic container), and filtration. Proper sizing depends on roof area and rainfall patterns. A diagram would illustrate the system components and their connections.
| Household Task | Water Usage (Liters/Day) |
|---|---|
| Showering | 50-100 |
| Toilet Flushing | 30-60 |
| Cooking & Cleaning | 20-40 |
| Gardening | Variable |
Waste Management and Composting in Off-Grid Environments
Effective waste management is vital for environmental protection in off-grid settings. Minimizing waste generation and employing appropriate composting methods are key.
Different Composting Methods, Green living off grid
Various composting methods are suitable for off-grid environments, including traditional pile composting, bin composting, and worm composting. The choice depends on factors like climate, space availability, and waste volume.
Strategies for Reducing, Reusing, and Recycling Waste
Reducing waste generation through conscious consumption, reusing items whenever possible, and recycling materials are essential components of sustainable waste management. This often involves creative solutions and resourcefulness.
Importance of Proper Waste Disposal
Proper waste disposal is crucial to prevent environmental contamination. Improper disposal can lead to soil and water pollution, attracting pests, and negatively impacting local ecosystems.
Innovative Off-Grid Waste Management Solutions
Innovative solutions include anaerobic digesters for converting organic waste into biogas, and greywater recycling systems for reusing wastewater for non-potable purposes.
- Step 1: Choose a location with good drainage.
- Step 2: Build a wooden frame or use existing materials.
- Step 3: Line the bin with wire mesh or hardware cloth to prevent pests.
- Step 4: Layer organic materials (brown and green).
- Step 5: Regularly turn the compost to aerate it.
- Step 6: Add water as needed to maintain moisture.
- Step 7: Harvest the finished compost after several months.
Sustainable Food Production in Off-Grid Settings
Sustainable food production is a cornerstone of off-grid living. Various methods can be employed, depending on available resources, climate, and personal preferences.
Methods of Sustainable Food Production
Gardening, hydroponics (growing plants in nutrient-rich water), and aquaponics (combining hydroponics with fish farming) are common methods. Each has its advantages and disadvantages concerning resource requirements and yields.
Challenges and Opportunities of Growing Food Off-Grid
Challenges include unpredictable weather, pest control, and limited access to resources. Opportunities include increased food security, reduced reliance on external food systems, and connection to nature.
Examples of Successful Off-Grid Food Production Systems
Numerous examples exist of successful off-grid food production systems. These demonstrate the adaptability of different methods to diverse environments and conditions. Researching specific case studies provides valuable insights.
Plan for a Small-Scale Off-Grid Garden
A small-scale garden might include a mix of vegetables, herbs, and fruits suitable for the local climate. Crop selection should consider factors like growing season, water requirements, and pest resistance.
| Crop | Yield (kg/m²) | Water Requirement (L/m²/day) |
|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | 5-10 | 5-10 |
| Lettuce | 2-4 | 3-5 |
| Potatoes | 10-20 | 8-12 |
Building Materials and Construction for Green Off-Grid Dwellings
Sustainable building materials and energy-efficient design are crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of off-grid dwellings.
Sustainable Building Materials
Recycled materials (e.g., reclaimed wood, recycled metal), natural materials (e.g., cob, straw bales, timber), and locally sourced materials reduce transportation costs and environmental impact.
Importance of Energy Efficiency in Off-Grid Building Design
Energy efficiency is critical to minimize energy consumption. This involves using appropriate insulation, passive solar design, and minimizing thermal bridging.
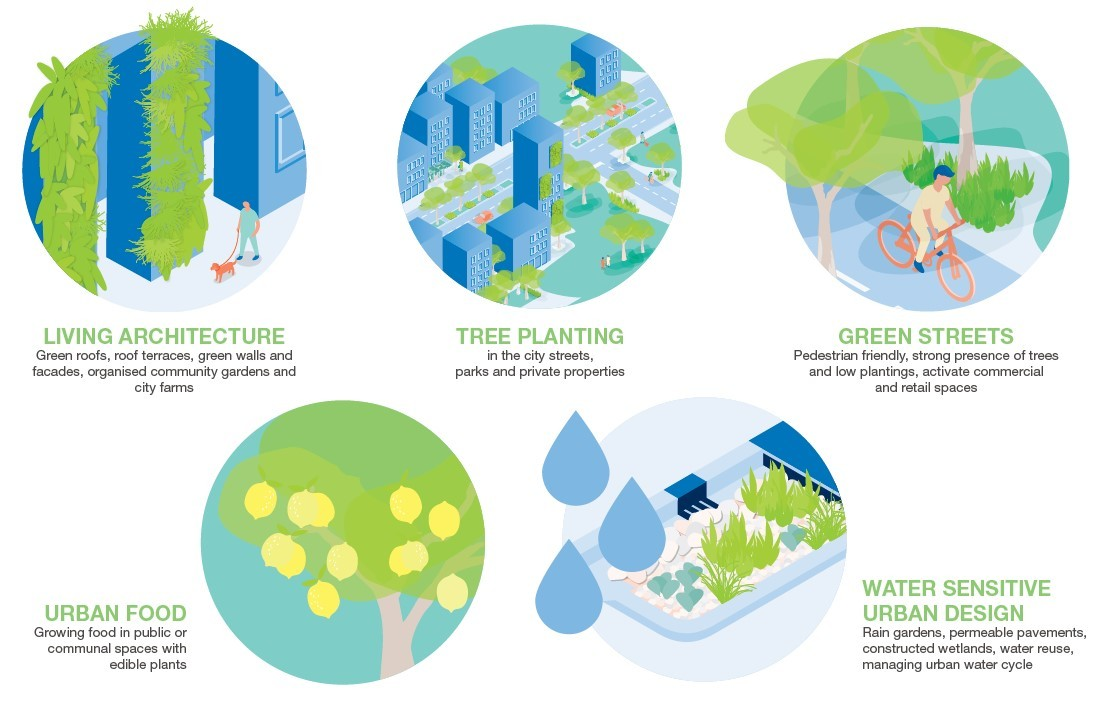
Eco-Friendly Building Techniques
Source: squarespace-cdn.com
Eco-friendly techniques include passive solar heating and cooling, natural ventilation, and rainwater harvesting for greywater recycling.
Design of a Small Off-Grid Dwelling
A small off-grid dwelling might incorporate sustainable materials and energy-efficient design principles. The following Artikels a conceptual design.
Foundation: Rammed earth, providing thermal mass and stability.
Walls: Insulated straw bales, offering excellent insulation and natural aesthetics.
Roof: Green roof with sedum plants, providing insulation, water retention, and aesthetic appeal.
Windows: Double- or triple-glazed windows to minimize heat loss.
Challenges and Considerations of Green Off-Grid Living: Green Living Off Grid
Several challenges are associated with off-grid living, requiring careful planning and preparation. Addressing these challenges proactively ensures a successful and sustainable lifestyle.
Potential Challenges Associated with Off-Grid Living
Challenges include access to resources, maintenance of systems, safety concerns (e.g., power outages, water contamination), and financial implications.
Importance of Community Support and Resource Sharing
Community support and resource sharing are invaluable for overcoming challenges and fostering resilience. Sharing knowledge, skills, and resources strengthens the community and enhances sustainability.
Financial Implications of Adopting a Green Off-Grid Lifestyle
Initial investment in off-grid systems can be substantial. However, long-term savings on utility bills and reduced reliance on external resources can offset these costs.
Categorizing and Providing Solutions for Challenges
Challenges can be categorized into technical (system maintenance, energy production), logistical (access to resources, transportation), and social (community support, skills acquisition) aspects. Solutions involve careful planning, appropriate technology selection, community collaboration, and continuous learning.
Last Word
Embracing green living off grid presents a unique opportunity to reconnect with nature and live more sustainably. While challenges exist, the rewards – from reduced environmental impact to increased self-reliance and a stronger connection with the natural world – are substantial. As technology advances and communities share knowledge and best practices, the path towards sustainable, off-grid living becomes increasingly accessible and attractive, offering a compelling vision for a future where environmental stewardship and personal autonomy converge.
